# Introduction
Note, these are WIP instructions. More details coming soon!
# The Speckle Viewer: Getting Started
You can download the package here (opens new window)!
For development purposes, to start a webpack live reload server run:
npm run serve
You can now access the example at http://localhost:9000/example.html (opens new window).
To build the library, you should run:
npm run build
# API
Syntax and examples for supported API methods. The examples assume a Viewer instance named v.
# Load/Unload an Object
v.loadObject( objectUrl ) / v.unloadObject( objectUrl )
Example: v.loadObject( 'https://speckle.xyz/streams/3073b96e86/objects/e05c5834368931c9d9a4e2087b4da670' )
# Get Properties of Loaded Objects
v.getObjectsProperties()
This returns a dictionary with { propertyName: propertyInfo } elements. The property information provided is:
type( =='string'/'number'/'boolean'): the property typeobjectCount(int): How many objects in the scene have this propertyallValues(array ofobjectCountelements): The values for this property of all objects that have this propertyminValue- the smallest value (using<operator, works also on strings)maxValue- the largest valueuniqueValues- a dictionary of{ uniqueValue: occurrenceCount }elements, specifying how many objects have the property set to that specific value
# Filtering and Colouring
Those calls filter and color the objects loaded in the scene, and drops the previous applied filters (filtering is not additive).
Syntax: await v.applyFilter( { filterBy, colorBy, ghostOthers } )
The 3 optional parameters are:
filterBy: A dictionary that specify the filter. Elements are in the form{ propertyName: propertyValueFilter }. The propertyValueFilter can be one of:- A specific value: (only objects with that property value pass the filter)
- An array of values: An object passes the filter if its value is in the array
- A range of values, specified by
{ 'gte': value1, 'lte': value2 }(greater than or equal, lower than or equal) - An exclusion list, specified by
{ 'not': excludedValuesArray }
colorBy: A dictionary that makes all objects colored based on a property value. Two types of coloring are supported:- Gradient (from a numeric property):
{ 'type': 'gradient', 'property': propertyName, 'minValue': propertyMinValue, 'maxValue': propertyMaxValue, 'gradientColors': [color1, color2] } - Category (for coloring each unique value differently):
{ 'type': 'category', 'property': propertyName, 'values': { value1: color1, value2: color2, ... }, 'default': colorForAnyOtherValue }. Thevaluesand thedefaultparameters are optional: Random colors are generated if they are omitted.
- Gradient (from a numeric property):
ghostOthers: A boolean (defaultfalse). If set totrue, then the objects that are filtered out are actually shown with very low opacity, so that the remaining objects have a better context.
To remove all filters: await v.applyFilter( null )
Examples:
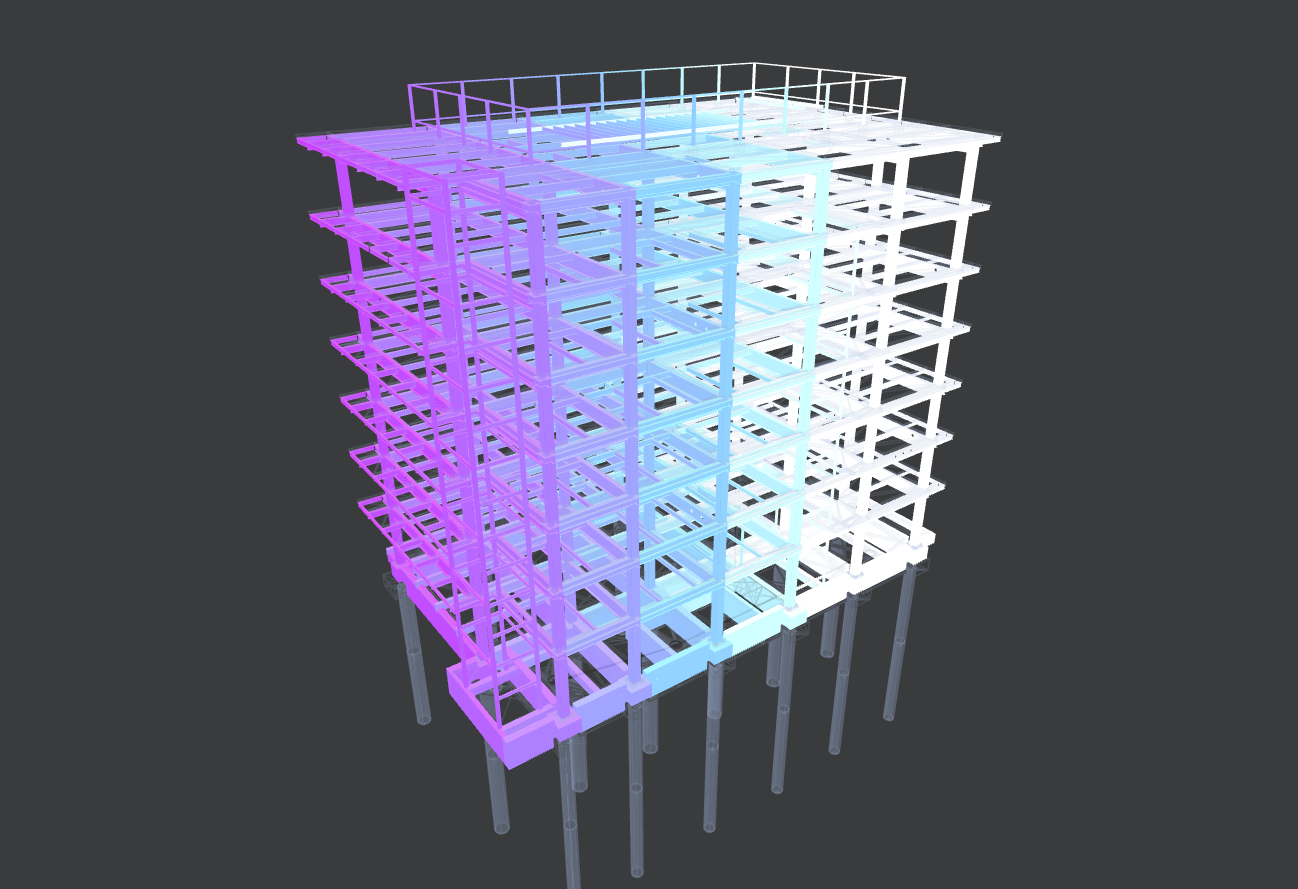
- filter and color levels by name
v.applyFilter({filterBy: {'level.name': ['3FL', '4FL', '7FL']}, colorBy: { property: 'level.name', type: 'category', values: {'3FL': '#F0FFFF', '4FL': '#6495ED', '7FL': '#7B68EE'} }, ghostOthers: true } )
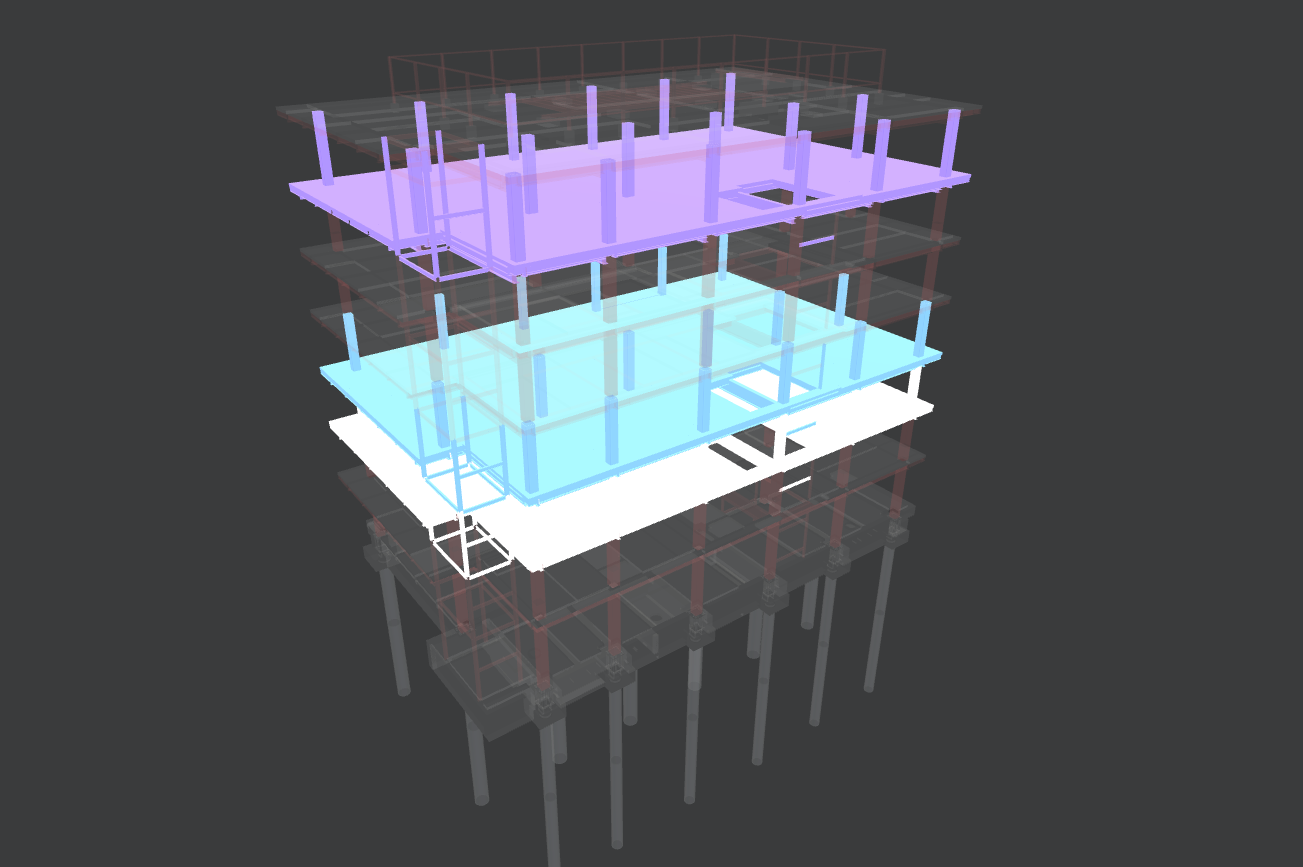
- color by property (e.g. 'baseLine')
v.applyFilter({colorBy: { property: 'baseLine.start.x', type: 'gradient', minValue: -7200, maxValue: 33000, 'gradientColors': ['white', 'CornflowerBlue', 'BlueViolet'] } } )